Mastopexy (Breast Lifting)
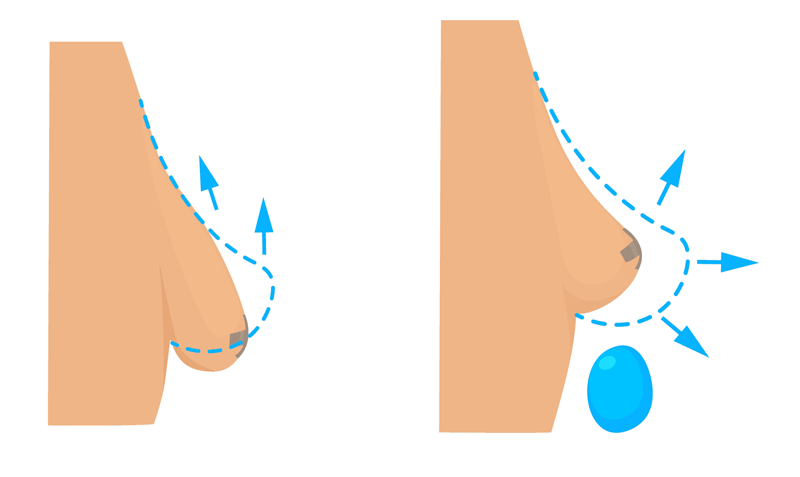
Breast mastopexy, commonly known as breast lifting, is a surgical procedure designed to elevate and reshape sagging breasts. Over time, factors such as aging, pregnancy, breastfeeding, weight fluctuations, and gravity contribute to the loss of breast firmness and shape. Mastopexy aims to restore a youthful, uplifted appearance by removing excess skin, tightening the surrounding tissue, and repositioning the nipple-areolar complex.
VARIABLE APPROACH
“Circumareolar” to “Anchor” Resection
It is true that small surgeries cannot achieve great results. The greater the amount of skin removed, the greater the lifting, but instead, the recovery period is longer, big scars and the incidence of complications increases. It is important to discuss the lifting method thoroughly with the patient.
- Periareolar Mastopexy (Circumareolar, Donut, or Benelli Mastopexy): Involves skin tightening, contouring, and elevation of the nipple-areola complex. A “donut” of skin is removed from around the areola, converting a larger areola to a smaller one. This technique is suitable for minimal breast sagging.
- Lollipop Mastopexy: A breast lift approach where the incision encircles the areola and extends down to the crease at the lower part of the breast, resembling a lollipop shape.
- Inverted-T or Anchor Mastopexy: The most common technique, involving circumareolar and vertical incisions extending to the lower breast crease. This allows for optimal breast positioning, resulting in a more natural shape. However, the recovery period is about two weeks, and frequent wound healing processes are required.
- Liposuction and Mastectomy: In cases where the mammary gland or fat is too large, liposuction and mastectomy may be required. When this occurs, beyond mastopexy, it may be considered “Breast Reduction” surgery.

Recovery Process by Procedure Type
- First Few Days: Patients may experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort, which can be managed with prescribed pain medication.
- First Week: Compression garments are recommended to minimize swelling and support healing.
- 2-3 Weeks Post-Surgery: Light activities can be resumed, but strenuous exercise should be avoided.
- 4-6 Weeks: Most of the swelling subsides, and patients can gradually return to normal activities.
- Scarring: While incisions will initially appear red, they will fade over time with proper care.
The Role of Implants in Mastopexy
In some cases, mastopexy alone may not provide the desired breast volume. Patients who desire fuller breasts may opt for breast implants (augmentation mastopexy). This combination procedure enhances both the position and volume of the breasts, providing a more comprehensive aesthetic result. However, implant placement should be carefully discussed with the surgeon to determine the best approach based on individual anatomy and goals.
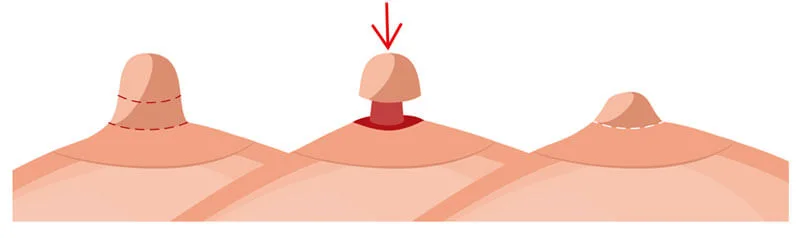
Nipple and Areola Reduction
In addition to lifting the breasts, some patients choose to undergo nipple or areola reduction to achieve better proportion and symmetry. These procedures can be performed simultaneously with mastopexy to refine the overall aesthetic outcome.
- Nipple Reduction: Involves decreasing the height or diameter of the nipple.
- Areola Reduction: Focuses on reducing the size of the pigmented skin surrounding the nipple to create a more balanced look.
Dr. Francis Jeon’s Perspective on Breast Lifting
“Of course, the more skin we remove, the greater the lifting effect. However, this also results in more noticeable scars. This is a double-edged sword, and it is crucial for patients to fully understand their expectations and outcomes before selecting a surgical method.”