Gynecomastia: Understanding the Facts
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia, commonly referred to as “man boobs,” is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of male breasts similar to female breasts. Men experiencing gynecomastia often notice their chest muscles fail to develop properly, even with dedicated exercise and strength training.
Clinically, gynecomastia presents as a firm or rubbery mass extending outward from the nipple, typically symmetrical on both sides.
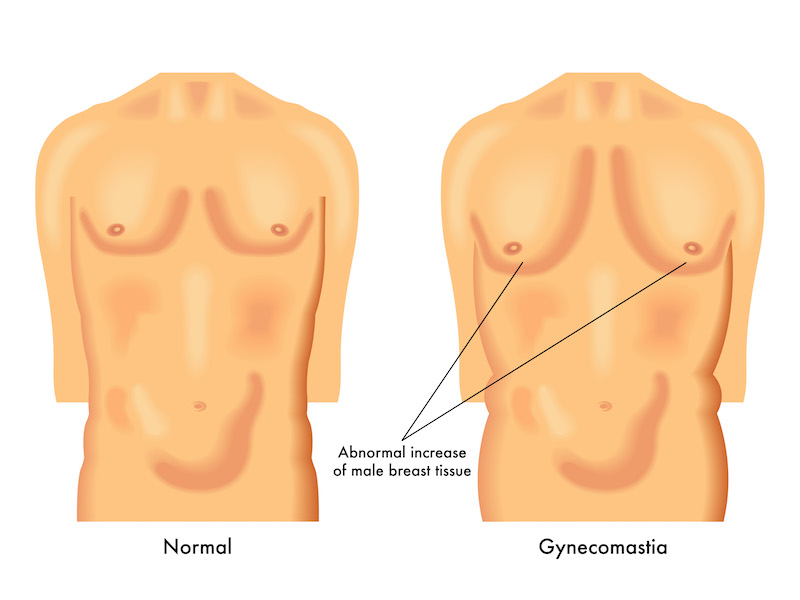
True Gynecomastia vs. Pseudogynecomastia
It’s important to distinguish between true gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia:
- True Gynecomastia: Characterized by excess mammary gland tissue along with fatty tissue.
- Pseudogynecomastia: Mainly composed of fat deposits without significant glandular tissue proliferation. However, clinical experience suggests that pseudogynecomastia is quite rare because, in most cases, fat accumulation in the chest area also leads to concurrent glandular enlargement.
True gynecomastia usually does not respond to diet or exercise, while pseudogynecomastia can improve significantly with weight loss and regular physical activity.
How Does Gynecomastia Occur?
Initially, both male and female breast tissues are identical before birth because humans are mammals. During puberty, approximately 20-30% of males experience temporary breast tissue enlargement due to hormonal fluctuations involving estrogen and androgen, which typically resolves naturally. However, in gynecomastia cases, breast enlargement persists or reoccurs, occasionally accompanied by breast tenderness or lumps.
Is Gynecomastia Dangerous?
Generally, gynecomastia is benign and poses no serious health risks. Male breast cancer, while possible, is exceedingly rare, accounting for less than 0.005% of male cancers and only 1% of all breast cancer cases. However, gynecomastia in adulthood can significantly impact self-confidence and body image, causing men to feel self-conscious and embarrassed about their appearance. This often leads to reluctance in participating in outdoor activities, exercising, or situations where their physique might be visible, thus negatively affecting their overall quality of life.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia arises primarily due to hormonal imbalances:
- Elevated estrogen (estradiol)
- Reduced testosterone levels
Common causes include:
- Physiological changes during puberty or aging
- Systemic conditions (liver cirrhosis, chronic renal insufficiency)
- Medications (cimetidine, marijuana, thiazide diuretics, omeprazole, tricyclic antidepressants, spironolactone, diazepam, anabolic steroids, exogenous estrogen)
- Rarely, tumors or unknown causes
Three Common Phases of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia can appear at any age but frequently occurs during:
- Neonatal Period: Resulting from maternal hormones transferred to the newborn.
- Puberty: Often idiopathic (unknown cause) and temporary.
- Older Adulthood: Typically associated with medication side effects, hormonal imbalance, tumors, liver or kidney diseases.
Fun Knowledge of Science: Digit Ratio and Gynecomastia
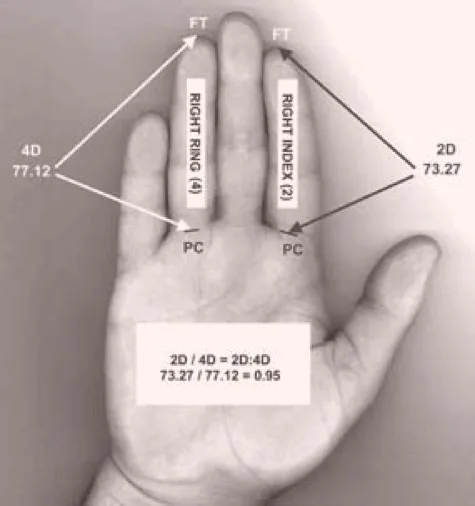
Did you know? At Evita Clinic, we measure your digit ratio—the length of your ring finger compared to your index finger—before your consultation. This quirky yet fascinating test indicates the level of androgen exposure you experienced in the womb. Higher androgen exposure often results in a longer ring finger relative to the index finger, offering interesting insights into hormonal factors linked to gynecomastia.


![[FAQ] Can I Have Gynecomastia Surgery and Abdominal Liposuction at the Same Time?](https://evitaclinic.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/gyn_tummy_same-500x383.webp)

