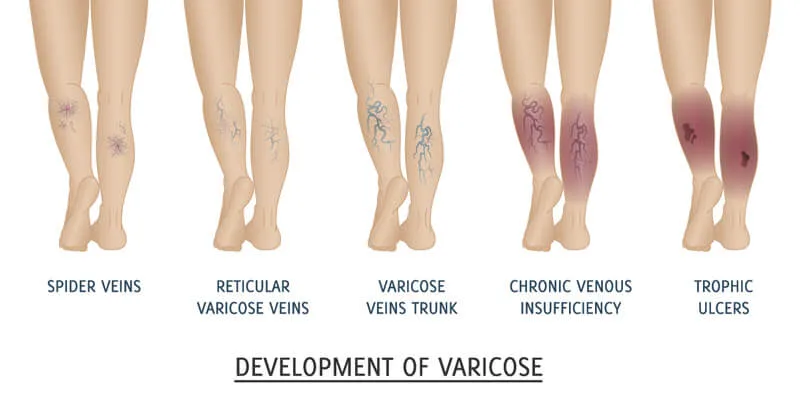
WHAT IS VARICOSE VEIN?
Varicose Vein
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that form just beneath the skin’s surface, most commonly in the legs and ankles.
They develop when the valves within the veins weaken or malfunction, causing blood to pool rather than flow efficiently back to the heart.
As pressure builds, the veins become stretched, swollen, and visibly distorted.
While often considered a cosmetic concern, varicose veins can sometimes lead to discomfort, swelling, and, in some cases, more serious circulatory complications if left untreated.
Symptons of Varicose Vein
Varicose veins often run in families, and the risk increases with age. Factors such as obesity, pregnancy, or jobs that require prolonged standing can put additional pressure on the leg veins, contributing to their development.
Varicose veins typically appear as dark blue, swollen, and twisted veins just beneath the skin. While some people experience no symptoms, others may notice mild to severe discomfort.
Mild Symptoms:
- A feeling of heaviness, burning, aching, or fatigue in the legs, which may worsen after prolonged standing or sitting.
- Swelling in the feet and ankles.
- Itching around the affected veins.
More Serious Symptoms:
- Persistent leg swelling.
- Calf pain and increased swelling after extended periods of sitting or standing.
- Skin changes, including discoloration, dryness, thinning, or inflammation.
- Scaling or the formation of open sores.
- Bleeding from minor injuries due to weakened skin.
Varicose veins are common and, in most cases, not a serious medical concern. However, managing symptoms early can help prevent complications and improve comfort.
Diagnosis of Varicose Veins
Diagnosing varicose veins typically involves a physical examination and, if necessary, imaging tests to assess the condition of the veins and blood flow.
1. Physical Examination
A doctor will begin by visually inspecting the affected veins while you are standing or sitting. They may ask about symptoms such as leg pain, swelling, or discomfort, and review your medical history, including risk factors like family history, pregnancy, or lifestyle habits.
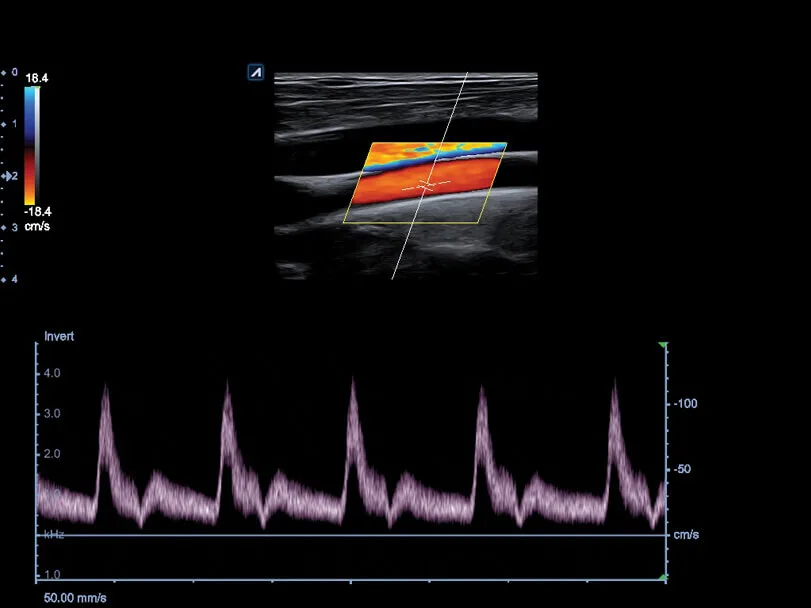
2. Doppler Ultrasound
If further evaluation is needed, a Doppler ultrasound is commonly used. This non-invasive test utilizes sound waves to visualize blood flow in the veins and detect valve dysfunction, blockages, or blood clots (deep vein thrombosis – DVT).
3. Venous Duplex Ultrasound
A more detailed version of Doppler ultrasound, this test provides both structural and functional assessments of the veins. It helps identify reflux (backward blood flow) and determine the severity of varicose veins.
4. Additional Diagnostic Tests (If Necessary)
In rare cases, additional imaging tests such as venography (using contrast dye to highlight veins on X-rays) or MRI/CT scans may be used to evaluate more complex venous conditions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Varicose veins are often harmless, but if you experience persistent pain, swelling, skin ulcers, or signs of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), seeking medical evaluation is crucial to prevent complications. Early diagnosis can help determine the best treatment options and prevent worsening symptoms.
Treatments for Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are a progressive condition, meaning they tend to worsen over time if left untreated. While medical treatments can effectively manage symptoms and improve appearance, prevention and lifestyle changes are the most crucial aspects of long-term management. Even after treatment, patients must adopt healthy habits to prevent recurrence and maintain good venous circulation.
1. Lifestyle Modifications: The Key to Prevention and Long-Term Success
ince varicose veins develop due to poor circulation and increased pressure in leg veins, modifying daily habits is essential to both prevention and post-treatment care. Even if you undergo medical treatment, failing to change your lifestyle may lead to recurrence.
Essential Lifestyle Changes for Varicose Veins
-
Wear Compression Stockings
- Helps improve circulation by providing gentle pressure that supports vein function.
- Recommended for individuals who stand or sit for long hours.
-
Elevate Your Legs Regularly
- Raising your legs above heart level for 15–20 minutes several times a day reduces swelling and venous pressure.
- Especially important for those experiencing leg fatigue or swelling after long periods of standing.
-
Stay Active & Exercise Regularly
- Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling strengthen calf muscles, which help pump blood back to the heart.
- Avoid sitting or standing for prolonged periods; incorporate movement into your daily routine.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Excess weight increases pressure on leg veins, worsening varicose veins and increasing the risk of recurrence.
- A balanced diet rich in fiber and antioxidants can support vascular health.
-
Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing
- If your job requires standing for long hours, shift weight between legs and take breaks to move.
- If sitting for extended periods, flex and extend your feet or stand up periodically to promote circulation.
-
Stay Hydrated & Eat a Vein-Friendly Diet
- Drinking plenty of water and consuming foods rich in flavonoids (citrus fruits, berries) can strengthen vein walls.
- Reduce salt intake to prevent fluid retention and leg swelling.
Prevention is key! Without lifestyle changes, even successfully treated varicose veins can return. Long-term commitment to these habits is essential for maintaining healthy legs.
2. Medical Treatments for Varicose Veins
If varicose veins cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns, minimally invasive procedures can effectively treat the condition. These procedures are typically performed on an outpatient basis with minimal recovery time.
Non-Surgical & Minimally Invasive Procedures
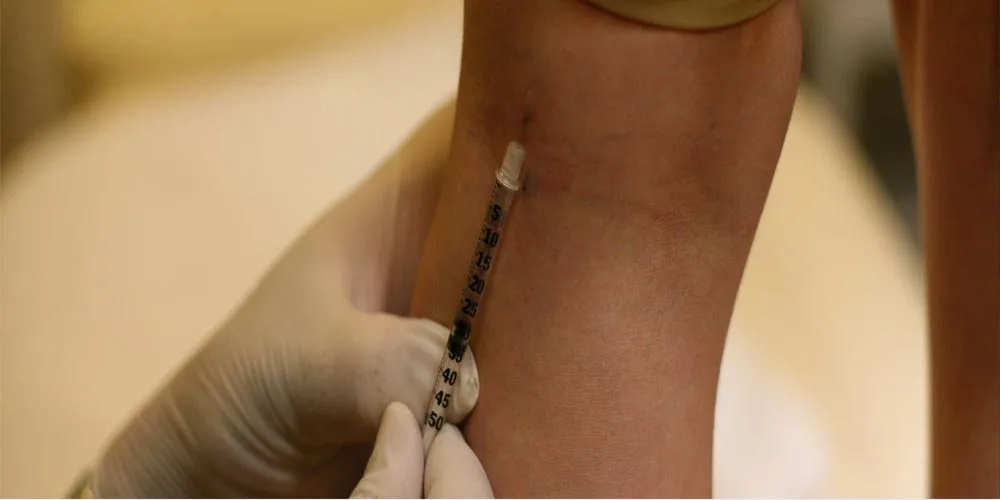
- Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is injected into small varicose veins, causing them to collapse and fade over time.
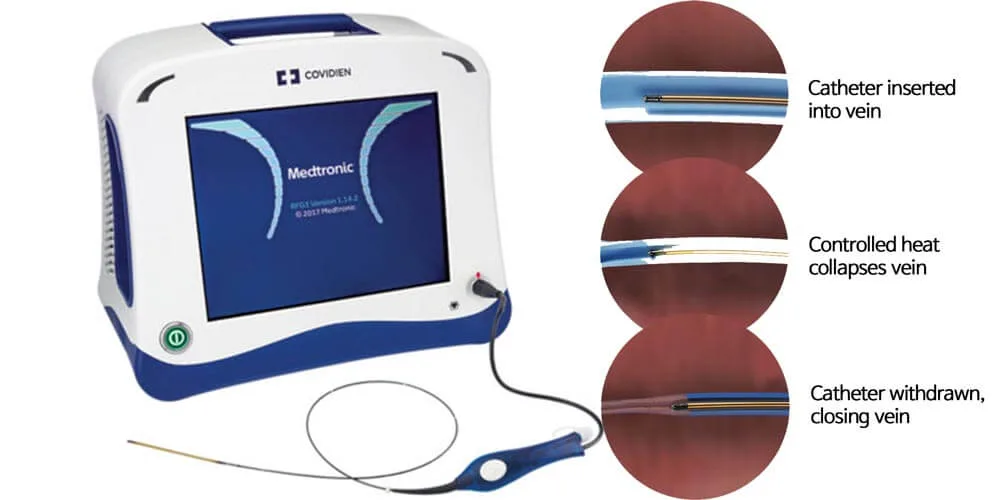
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA) & Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Heat energy is delivered through a catheter to close off diseased veins.
- Venaseal™ (Medical Adhesive Treatment): A specialized medical adhesive is injected into the vein to seal it shut, eliminating the need for heat-based treatments or compression stockings post-procedure.
Surgical Treatments (For Severe Cases)
In advanced cases, surgery may be necessary when minimally invasive treatments are ineffective.
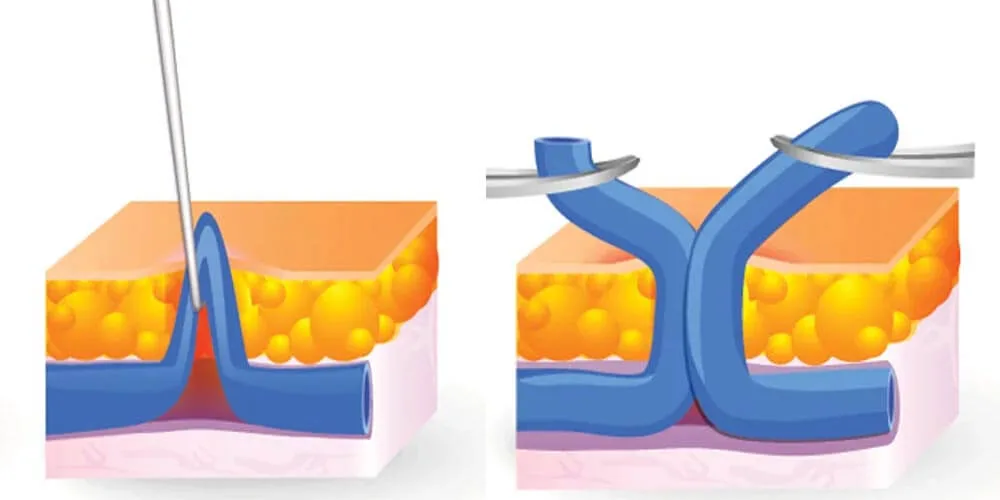
- Phlebectomy: Small varicose veins are removed through tiny incisions.
- Vein Stripping & Ligation: Larger varicose veins are surgically tied off and removed.
Due to the advancements in less invasive treatments like Venaseal™, EVLA, and RFA, traditional surgery is rarely required today.
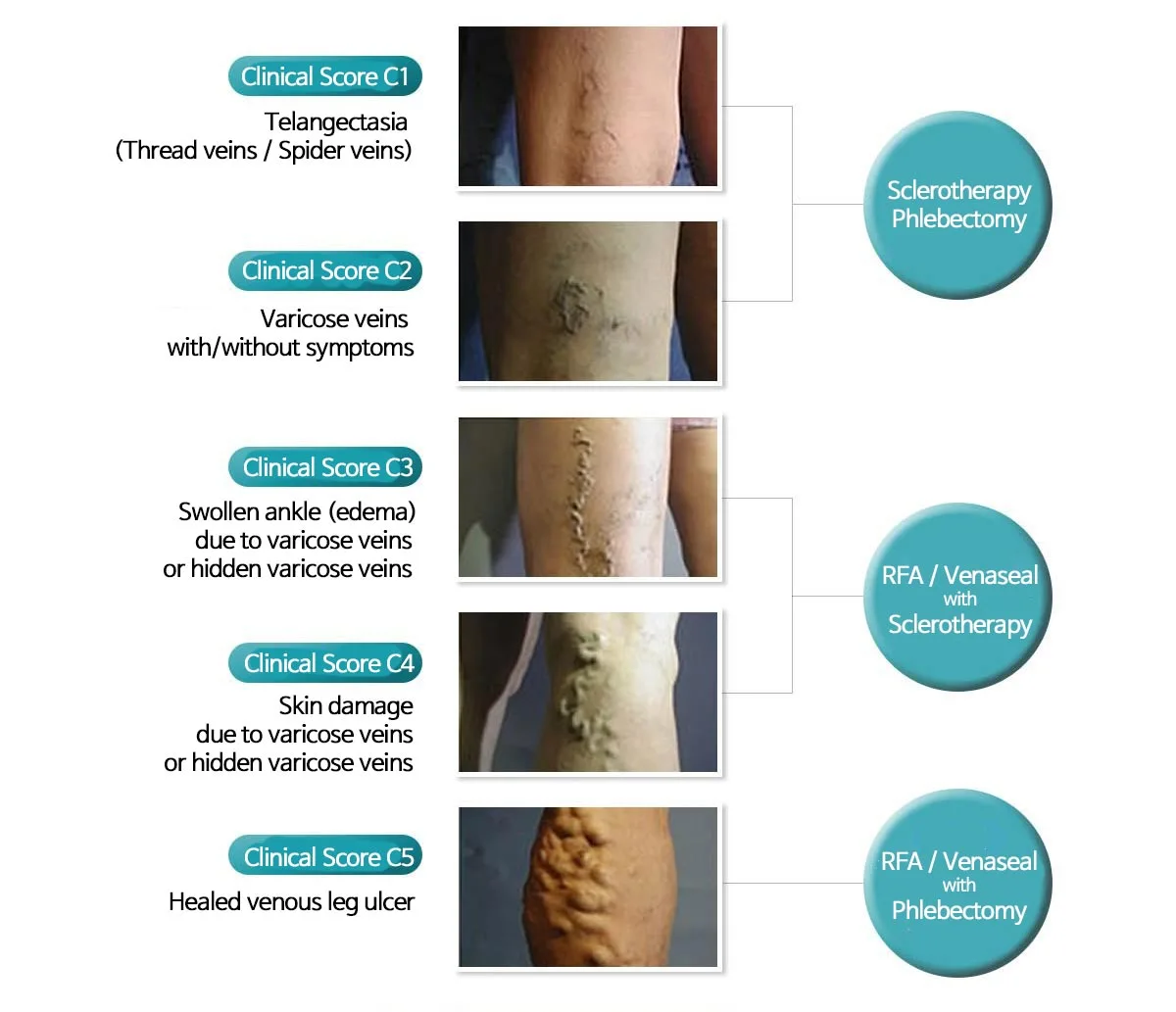
Comprehensive Classification System for Chronic Venous Disorders (CEAP) & Treatments

VARIABLE VARICOSE VEIN
Variable Treatments
VenaSeal
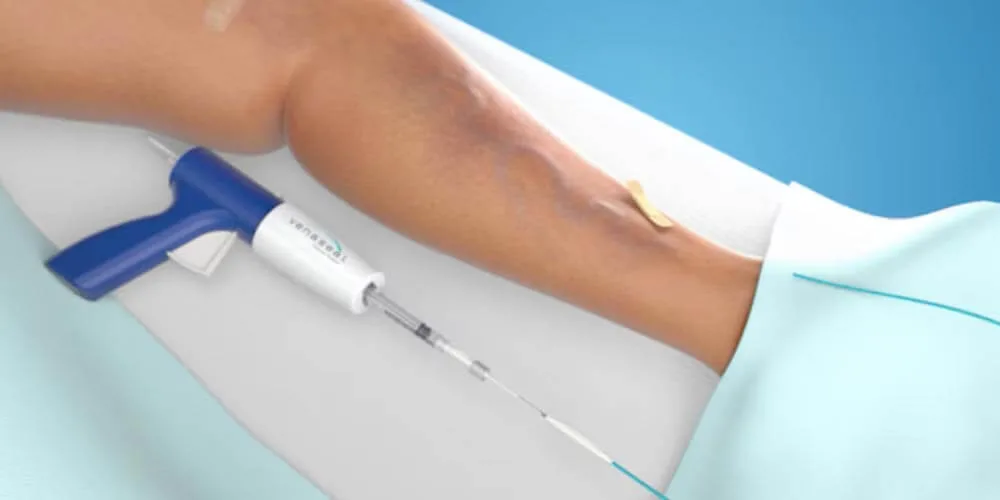
The Venaseal™ procedure utilizes a medical adhesive to effectively and permanently seal varicose veins without the need for heat-based energy.
- Minimally invasive with no need for tumescent anesthesia
- Suitable for various vein sizes, including the greater & lesser saphenous vein
- Immediate return to daily activities with minimal downtime
Before & After
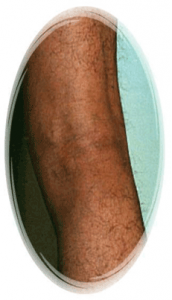
36 years old man, After phlebectomy, 4 weeks later
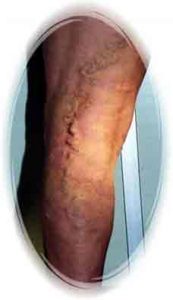
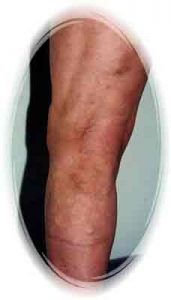
62 years old woman, After EVLT, 11 weeks later
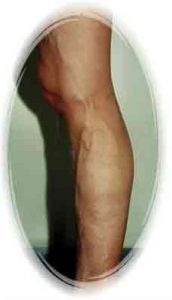
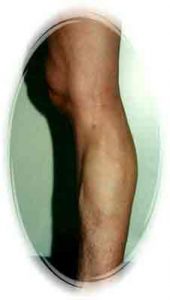
19 years old man, After phlebectomy & sclerotherapy, 6 weeks later
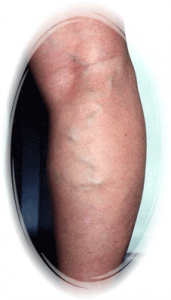

50 years old woman, After sclerotherapy, 8 weeks later
The Importance Of Compression Stocking

Compression Therapy for Varicose Veins and Lymphedema
Compression therapy involves the use of specialized compression stockings to effectively manage varicose veins and lymphedema, promoting better circulation and reducing swelling.
How Gradient Compression Works
Gradient elastic stockings, first developed in the early 1950s by an engineer and patient, remain the gold standard for managing chronic venous disease. These stockings apply graduated pressure, which is strongest at the ankle and gradually decreases up the leg. This controlled compression helps:
- Prevent excessive expansion of superficial veins.
- Reduce blood pooling and backward flow, minimizing congestion.
- Alleviate symptoms such as leg discomfort, swelling, and varicose veins.
The Importance of Prevention
When it comes to varicose veins, prevention and recurrence prevention are just as important as treatment. Even after medical intervention, consistent use of compression stockings can help maintain healthy circulation and reduce the risk of future vein problems.
Where to Buy
To ensure the best quality and effectiveness, we recommend purchasing compression stockings from Evita Clinic or trusted online retailers.
Why Prevention & Lifestyle Changes Matter
✅ Varicose veins are progressive – early prevention is crucial.
✅ Even after treatment, recurrence is possible without lifestyle modifications.
✅ Simple habits like leg elevation, compression stockings, and exercise can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent new varicose veins.
Taking control of your vein health through lifestyle changes and early intervention is the best way to ensure long-term success in managing varicose veins. Treatment can help, but your daily habits will determine the long-term outcome!